Securing OTT Content with Multi-DRM & Forensic Watermarking
OTT (Over-The-Top) content is rapidly transforming the entertainment landscape. With the internet and TV converging like never before, the way people search, share and watch their favorite content is evolving. But the growing popularity has made the OTT landscape a battlefield no less.
There is a drastic surge in the number of OTT players in the industry. While the likes of Netflix and Amazon Prime Video already have a considerable subscriber base, Apple, Disney, Comcast, and AT&T are all set to launch their streaming services. Streaming war is in all its glory with the rising competition.
But apart from the competition, protecting the OTT content is another cause of concern for the OTT platforms. As per a report by Parks Associates, piracy could cost US pay-TV and OTT operators $12.5 billion in lost revenue in 2024. DRM or Digital Rights Management could be an effective way of securing OTT content and preventing their piracy and unauthorized use.
History of Online Streaming
Online streaming is an intricate technology overflown with a host of complex terms. One that you’d commonly come across is IPTV (Internet Protocol Television). The traditional methods of content broadcasting like satellite or cable TV are experiencing a shift in paradigm with the growing popularity of internet-based content streaming, and IPTV has played a significant role in this transition.
It was in 1995 that Percept Software created an internet-based video product for Windows and Unix and named it IP/TV. The software was able to transmit single as well as multi-source video and audio traffic of up to DVD quality. This laid the foundation for OTT content that the consumers are currently so passionate about.
However, piracy was a threat then, and it continues to be a major risk for modern OTT platforms now. But over the years, the DRM technologies too have advanced by leaps and bounds to help OTT platforms securely distribute their content while also improving their reach across devices.
Related Article – Introducing PallyCon for OTT
Why Secure OTT Content?
While media houses are fighting a fierce battle with each other to grab a bigger share of the OTT pie, it’d be logical for them to combine their resources to ward off a threat that no online video platform is immune to- video piracy.
While it seemed like video piracy was a thing of the past at least for a while, it is rearing its head again and is more powerful and advanced this time around. Despite the industry-wide efforts to standardize digital content and improve security, device fragmentation poses a significant challenge in avoiding video piracy.
Securing Multiple Devices
In the past, when it was just pay-TV that delivered premium content, it was easier for the content producers to secure and certify the devices that have access to the content. But modern mobile consumers wanted the flexibility of viewing their favorite content anywhere and anytime. OTT platforms fulfilled this demand.
While the eventual goal of OTT platforms is to reach newer consumers, this in itself proves to be a significant threat. From PCs, laptops, tablets, gaming consoles, to mobile phones, consumers use many different types of devices to access online video content. Unfortunately, most of these devices do not have adequate security to protect premium OTT content.
While a lot of modern video players do implement 3rd party DRM into their product, they do not have a comprehensive content protection provider for securing premium content. This is the reason why OTT platforms are now relying on Multi DRM solutions so that their premium content remains secure across devices.
Related Article – Analysis of VOD Piracy in OTT
Protecting Premium Content
MovieLabs, a joint venture of Paramount, Disney, Sony Pictures, Fox, Twentieth Century, and other media powerhouses, introduced advanced security recommendations to prevent piracy of paid video content. The pay-TV providers are now required to comply with the security recommendations of MovieLabs to be able to stream the content of these production houses.
Even online streaming of live events like sports, concerts, etc. is growing on popularity. But online streaming of live coverage requires adaptive bit-rate for seamless live streaming. The DASH Industry Forum then introduced MPEG-DASH or Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP to eliminate the complexities of live streaming content across devices while also keeping them secure.
Working of DRM
Most OTT platforms think of DRM as a way to encrypt the content. But while this is not untrue, DRM is more of a digital licensing system that enables content producers to control who or how accesses their online content. Encryption sure is an integral part of the DRM workflow, but there are other equally important aspects as you will find out in the subsections below-
-
Key Distribution/Storage
There are two different ways in which DRM is implemented for securing digital content. It is first applied in the packager for encrypting the content and then for decrypting the content to enable it to be streamed by paid users.
- Packager Encryption-
The packager requests for an encryption key from the DRM system for encrypting content. The generated encryption key is linked to the content ID. The packager then uses the key for encrypting and re-packaging the content. - Client Decryption-
When a paid user requests for particular content, it first needs to be decrypted so that the user can play the content. A decryption key for the content ID linked to the content is requested from the DRM system.
- Packager Encryption-
-
Tokens and Additional Security
While encryption is an excellent way to secure digital content, does it also prevent key and URL sharing? No, encryption in itself is not able to prevent piracy through the sharing of keys and URLs. But the DRM workflow has other functionalities to protect the content from these common sharing methods.
These functionalities are as follows-
- Tokens-
Tokens are used for validating the integrity and consistency of content requests. When a client requests content from the server, the originating request is validated with the help of the incoming token. This helps in preventing the sharing of URLs and tampering. - Entitlement-
While tokens can help prevent the problem of URL sharing, what if multiple clients use the same public IP address, like from a university or a workplace? For this, the entitlement systems are integrated into CMS (Customer Management Systems) to control the services that customers are eligible to access. For instance, the content platform can control how many parallel streaming sessions are allowed to an IP address. - HTTPs-
HTTPs are commonly used for content streaming. This helps the content platforms to ensure that the servers and clients are authenticated with one another, and the connection established between them is always secure. Even the traffic, along with the metadata, between the server and the clients, is encrypted to make the entire streaming session confidential and secure.
- Tokens-
Related Article – Multi-DRM – An Antidote to Video Piracy Landscape
Traditional Content Flow for Packaging
Traditionally, the whole packaging process where the source content in formats like MP4 is converted into formats like HLS or DASH was completed even before any client requested for the content. The encrypted content copy was always ready and stored in the streaming system. As and when a client requests for content, based on the request, the correct format of the content was sent for completing the request.
But this method requires a higher storage footprint as all the different pieces of content need to be encrypted in multiple formats. Apart from the streaming format, it also required content copies in various bitrates and resolutions. Just-in-time packaging technology helped overcome this challenge.
Just-in-Time Packaging
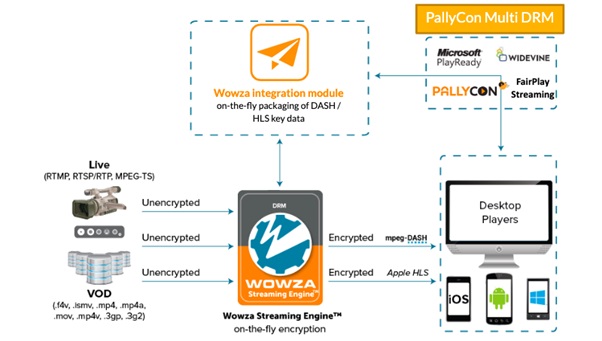
Many of the multi-DRM solutions available now package content “on the fly” or “just in time”. In other words, the content is packaged in a particular format as and when it is requested. Encryption too, follows the same “just in time” methodology in these systems.
When a client requests a particular content, the streaming system first inspects the client to know the right encryption DRM and streaming format requested. Based on the request, the system then repackages the existing content and encrypts the same before completing the request. Needless to say, all of this gets completed in less than a second so that the shorter latency of live streaming is adequately maintained.
Multi-DRM for Securing OTT Content
With the growing need to protect online content, there are now multiple DRM systems available for different devices, TVs, gaming consoles, and even browsers. Only content that complies with a particular DRM system can be streamed on that specific device/TV/gaming console/browser. Currently, there are 3 very popular DRM systems-
So, for a particular piece of content to be streamed across multiple devices, TVs, and browsers, and reach more consumers, the content needs to comply with various DRM systems. A multi-DRM system can be a cost-effective solution to achieve this compliance with multiple DRMs.
In simple words, multi-DRM systems have license management features for multiple DRMs like the ones listed above. This ensures that the content can be streamed and viewed across a larger number of devices, TVs, gaming consoles, and browsers.
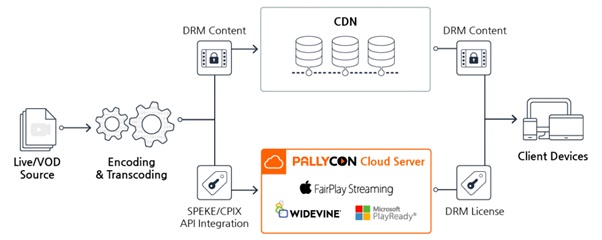
How Do Multi-DRM Systems Work?
Multi-DRM systems generally use the MPEG-CENC standard to enable a multiplicity of rights management across devices. It allows the association of a single content key to multiple DRMs in the most efficient manner. A single key is used for encoding and encrypting content, making it compatible with most popular DRM systems.
During the packaging step, the metadata of different DRMs is simultaneously added to complete the content request of the client. Individual DRMs are then responsible for license mappings and license acquisition of the content. The player used by the client then decides what DRM should be used for the playback.
Related Article – Learn how to integrate Multi-DRM on various platforms
Forensic Watermarking with Multi-DRM
The security of premium content, such as World Cup real-time relay channels or Hollywood studios’ high-definition movies, is becoming more and more important. In order to protect premium content from P2P piracy or illegal streaming services, it is necessary to apply forensic watermarking with the introduction of high-level copy protection(DRM, Digital Rights Management) technology.
PallyCon Forensic Watermarking solution can insert invisible user-specific information in real-time to video content, allowing content service providers to track the distributor from illegally distributed content.
The combination of multi-DRM and forensic watermarking helps secure the entire content value chain, effectively preventing piracy and enabling deeper market penetration.
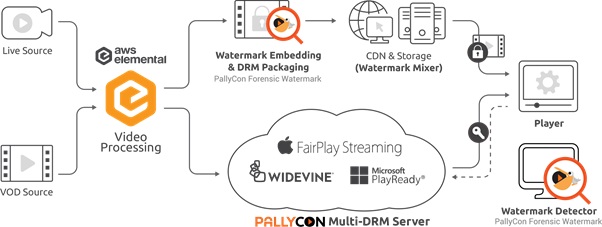
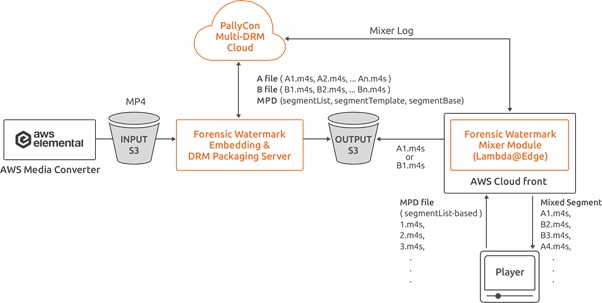
System Architecture
Cloud-based forensic watermarking service for VOD
- PallyCon Forensic Watermark Embedder module pre-processes source mp4 video file which is transcoded by AWS MediaConvert. Two sets of marked videos are generated and packaged as DRM-applied DASH / HLS contents.
- When client player downloads or streams the content, PallyCon forensic watermarking module combines A/B (0/1) versions of DASH / HLS segments real time to insert unique user information into the stream. Lambda@Edge modules running on AWS CloudFront edge servers are used to process the segments mixing.
PallyCon Forensic Watermarking system architecture on AWS
Conclusion
Content piracy is a global phenomenon and requires multiple technologies to work in parallel to deliver lasting prevention. Advanced multi-DRM systems and forensic watermarking should be at the root of every effective content security strategy implemented by OTT platforms.
Using such advanced solutions is the only way forward for OTT platforms to ensure content integrity, increase accessibility, and effectively monetize their premium content.

PallyCon provides cloud-based SaaS multi-DRM solution and Forensic Watermarking service. Cloud services built on AWS enables you to use services in the cloud. Get started contents protection quickly and easily with PallyCon.